Integrating Markdown into a static SvelteKit site
Integrating markdown .MD files into a SvelteKit project.
Prerequisites
This assumes you have a basic SvelteKit project setup, and are just looking for a way to integrate markdown files into your site. But for the sake of completeness, we can create one from scratch.
npm init svelte@latestThen just follow the defaults until the project is setup in the folder of your choice. We chose the SvelteKit demo app with TypeScript and no additional options.
npm install
npm run dev --openNow we should have the demo app running in the browser. 
Create some MD files
You can place these anywhere but lets add the files to src/lib/md/. Create a TopLevel.md here, then create a src/lib/md/folder/SecondLevel.md. I personally use Obisidan as a markdown editor, and thus this is more of a guide for mixing Obsidian vaults with a SvelteKit application. 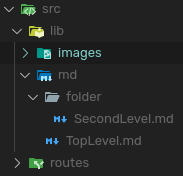
Markdown preprocessing
To include the markdown files into the Svelte build process, we need a markdown preprocessor. For this we can use mdsvex. Mdsvex has a bunch of neat features and helpers for working with Svelte and markdown, but most of these can be for niche use case, and for mixing svelte and markdown. We just want raw control of our markdown files at build time to create some neat things.
npm i -D mdsvexAnd then update svelte.config.js
import adapter from '@sveltejs/adapter-auto';
import { vitePreprocess } from '@sveltejs/vite-plugin-svelte';
import { mdsvex } from 'mdsvex';
const mdsvexOptions = {
extensions: ['.md'],
}
/** @type {import('@sveltejs/kit').Config} */
const config = {
// Consult https://kit.svelte.dev/docs/integrations#preprocessors
// for more information about preprocessors
preprocess: [vitePreprocess(), mdsvex(mdsvexOptions)],
extensions: ['.svelte', '.md'],
kit: {
adapter: adapter()
}
};
export default config;What this does is convert all the .md files in your project to Svelte components allowing you to render them in your pages as if they were just another .svelte file.
Handling metadata
Most markdown distributions allow Frontmatter syntax for adding some extra metadata to a markdown file. For example, lets augment our markdown files with a title. TopLevel.md
---
title: This is TOP
---
# Top H1
TopSecondLevel.md
---
title: Bottom
---
# Second H1
BottomWe can now use this data in our Svelte app for whatever we want when rendering it.
Using our markdown files
Now lets create a src/lib/md.ts file to include all our logic. As well as create a route to display our posts src/routes/md/[...slug]/+page.svelte and src/routes/md/[...slug]/+page.ts.
md.ts
export type Md = {
// this is the metadata for the file
metadata: Metadata;
// this is the default export of the file (the content of the file)
default: unknown;
};
export interface Metadata {
title: string;
};
function loadMDFiles() {
let records = import.meta.glob<Md>('/src/lib/md/**/*.md', { eager: true });
// convert to array
let entries = Object.entries(records).map(([path, record]) => {
// lets use the filename and directory as the slug
let slug = path.replace('/src/lib/md/', '').replace('.md', '');
return {
slug,
...record.metadata,
content: record.default
};
});
return entries;
}
export const md = loadMDFiles();/src/routes/md/[...slug]/+page.ts
import { md } from '$lib/md';
export const load = async ({ params }) => {
let post = md.find((post) => post.slug.toLowerCase() === params.slug.toLowerCase());
return post;
}/src/routes/md/[...slug]/+page.svelte
<script lang="ts">
export let data;
</script>
<!-- using the metadata -->
<h1>{data.title}</h1>
<!-- using the content -->
<svelte:component this={data.content}></svelte:component>Viewing the pages
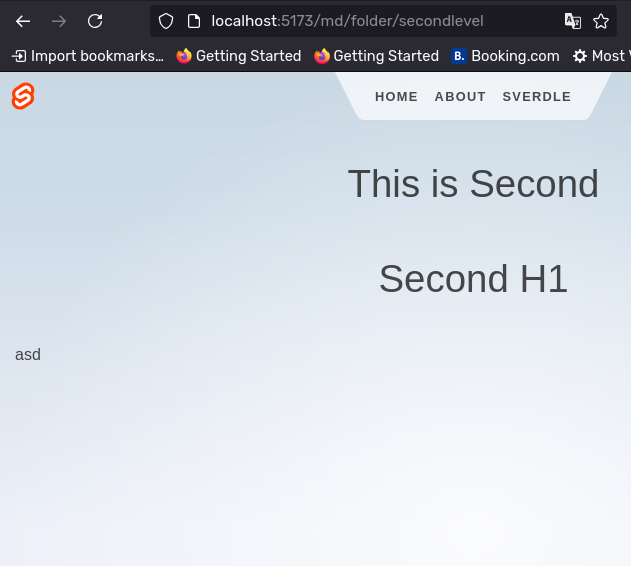
Now head over to http://localhost:5173/md/toplevel and http://localhost:5173/md/folder/secondlevel and you should see the content of your markdown files.